Many PLC-s also work with analog I/O devices. Analog devices use signals that are continuously variable within a specified range, such as 0 to 10 V DC or 4 to 20 mA. Analog signals are used to represent variable values, such as speed, rate of flow, temperature, weight, level, etc. In order to process an input of this type, a PLC must convert the analog signal to a digital value. Digital values from analog inputs are stored in addressable memory for use by the user program. Similarly, the user program can place digital values in addressable memory locations for conversion to analog values for the designated analog outputs.
Analog I/O points can be added using expansion modules for any CPU. The number of expansion modules depends on the CPU type and how many modules it can support. Expansion modules are available with 4 or 8 analog inputs, 2 or 4 analog outputs, or 4 analog inputs and 1 analog output (Or many other combinations, depending on the manufacturer and types). In addition, expansion modules are available for use with thermo-couples or RTD type sensors which sense the temperature at a specific point in a machine or process.
Analog Input Example
Analog inputs can be used for a variety of purposes. In the following example (Picture 1), a scale is connected to a load cell. A load cell is a device that generates an electrical output proportional to the force applied.
Picture 1: Analog Input Example
The load cell in this example converts a value of weight from 0 to 50 pounds into a 0 - 10 V DC analog value. The 0 - 10 V DC load cell signal is connected to an PLC’s analog input. The analog value applied to the PLC can be used in various ways. For instance, the actual weight can be compared to a desired weight for a package. Then, as the package is moved on a conveyor, the PLC can control a gate to direct packages of varying weight.
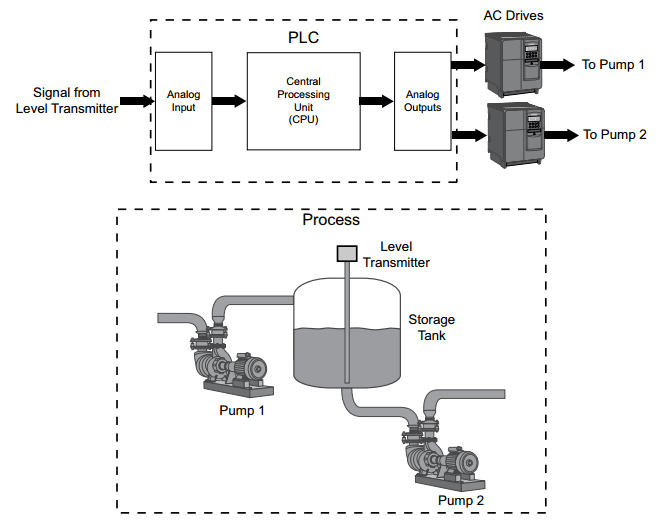
Analog Output Example
Analog outputs from a PLC are often supplied directly or through signal converters or transmitters to control valves, instruments, electronic drives or other control devices which respond to analog signals. For example, analog outputs from the PLC could be used to control the flow of fluid in a process by controlling AC drives (Picture 2). Rather than simply turning the AC drives on or off, which could be accomplished by discrete outputs, analog signals can be used to control the output of the AC drives. This would allow the speed of the pumps to be varied dynamically in response to changes in process requirements.
Picture 2: Analog Output Example

No comments:
Post a Comment